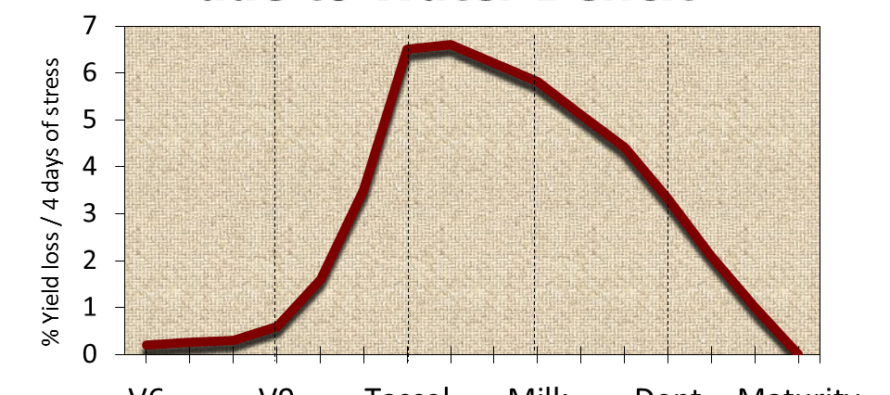
Will We Need to Irrigate Our Corn Again?
 Considering the abundant rainfall during June and the corn crop progressing closer toward maturity, many are wondering whether additional irrigation may even be needed – and some have not even rolled out poly pipe. Although corn water needs and sensitivity to stress definitely drop off considerably during late reproductive stages, it is a little early to assume this crop is made. This season’s corn is generally several days later than normal and fairly similar to the pace of last year’s crop, assuming similar planting dates. Thus, we anticipate our earliest corn in the South Delta region to begin reaching physiological maturity in late July, and later for areas further north or planted later. Thus, unless we continue to get some rain to help us out, we may still need to make some important irrigation and other management decisions before this crop is made. In fact, forgoing management practices which may mitigate severe stress or pest issues during late reproductive stages could potentially cut corn yield 15 to 50 bushels per acre, or profit $60 to $210 per acre. The bottom line is you don’t want to give up on the crop yet, if you can influence the crop outcome.
Considering the abundant rainfall during June and the corn crop progressing closer toward maturity, many are wondering whether additional irrigation may even be needed – and some have not even rolled out poly pipe. Although corn water needs and sensitivity to stress definitely drop off considerably during late reproductive stages, it is a little early to assume this crop is made. This season’s corn is generally several days later than normal and fairly similar to the pace of last year’s crop, assuming similar planting dates. Thus, we anticipate our earliest corn in the South Delta region to begin reaching physiological maturity in late July, and later for areas further north or planted later. Thus, unless we continue to get some rain to help us out, we may still need to make some important irrigation and other management decisions before this crop is made. In fact, forgoing management practices which may mitigate severe stress or pest issues during late reproductive stages could potentially cut corn yield 15 to 50 bushels per acre, or profit $60 to $210 per acre. The bottom line is you don’t want to give up on the crop yet, if you can influence the crop outcome.
 One of the most critical late-season management inputs during July is normally irrigation needs. Thankfully, corn moisture requirement steadily drops from a peak of 1.5-1.75 inches per week prior to the dough stage (four weeks post tassel) to an inch or less per week after dent and even lower as the grain approaches physiological maturity. This reduced crop moisture demand may allow you to scale back irrigation, as the crop approaches maturity. If you use our predominant furrow-irrigation systems, you likely can lengthen intervals between irrigation cycles to save expenses and prevent unnecessary saturation, which is harmful to the crop. For example, two well-timed irrigation events (shortly after dent and at 50% milk-line) should generally provide plenty of moisture for the corn crop during the last 20 days – as opposed to three weekly applications. Pivot irrigation volume may also be trimmed to adjust for reduced corn water use during latest growth stages. The key to proper irrigation timing is checking soil moisture using sensors or basic techniques, like a probe or shovel, rather than simply doing what you did last week. You also need to factor in reduced crop water demand and sensitivity as the crop matures. Weather, soil moisture and crop conditions can vary widely from field to field, week to week, and year to year, so we highly encourage you to closely monitor soil moisture level and schedule accordingly.
One of the most critical late-season management inputs during July is normally irrigation needs. Thankfully, corn moisture requirement steadily drops from a peak of 1.5-1.75 inches per week prior to the dough stage (four weeks post tassel) to an inch or less per week after dent and even lower as the grain approaches physiological maturity. This reduced crop moisture demand may allow you to scale back irrigation, as the crop approaches maturity. If you use our predominant furrow-irrigation systems, you likely can lengthen intervals between irrigation cycles to save expenses and prevent unnecessary saturation, which is harmful to the crop. For example, two well-timed irrigation events (shortly after dent and at 50% milk-line) should generally provide plenty of moisture for the corn crop during the last 20 days – as opposed to three weekly applications. Pivot irrigation volume may also be trimmed to adjust for reduced corn water use during latest growth stages. The key to proper irrigation timing is checking soil moisture using sensors or basic techniques, like a probe or shovel, rather than simply doing what you did last week. You also need to factor in reduced crop water demand and sensitivity as the crop matures. Weather, soil moisture and crop conditions can vary widely from field to field, week to week, and year to year, so we highly encourage you to closely monitor soil moisture level and schedule accordingly.
 Corn Irrigation Termination – You certainly do not want to terminate irrigation so that the crop stresses before corn physiological maturity (black layer) occurs (for more information see http://wp.me/p1jA50-iV.) When July rainfall fails to meet crop demand, water deficit resulting from premature irrigation termination will create considerable stress, prohibiting kernels from reaching their full potential size and weight. Although kernels outwardly appear mature and corn water use begins declining at the dent stage, this is far too early to terminate irrigation. Potential kernel weight is only about 75% complete at the dent stage. Thus, termination of irrigation at the dent stage might reduce grain yields as much as 15-20% (30-40 bu/a) when hot, dry conditions persist. Early irrigation termination will also likely reduce stalk strength and promote lodging, because plants will cannibalize energy from vegetative organs to fill kernels, when they are stressed.
Corn Irrigation Termination – You certainly do not want to terminate irrigation so that the crop stresses before corn physiological maturity (black layer) occurs (for more information see http://wp.me/p1jA50-iV.) When July rainfall fails to meet crop demand, water deficit resulting from premature irrigation termination will create considerable stress, prohibiting kernels from reaching their full potential size and weight. Although kernels outwardly appear mature and corn water use begins declining at the dent stage, this is far too early to terminate irrigation. Potential kernel weight is only about 75% complete at the dent stage. Thus, termination of irrigation at the dent stage might reduce grain yields as much as 15-20% (30-40 bu/a) when hot, dry conditions persist. Early irrigation termination will also likely reduce stalk strength and promote lodging, because plants will cannibalize energy from vegetative organs to fill kernels, when they are stressed.

This ear cross-section has the mik-line progressed half-way down the kernel. Thus, it needs moisture and other resources to carry it 10 days to reach physiological maturity.
Kernels mature from the outside-in when hard starch begins forming at the crown at the dent stage. The crown will turn hard and become the bright shiny golden yellow color of mature kernels. This starch and weight accumulation will steadily progress towards the base of the kernel (where it attaches to the cob) taking about 20 days to complete. The most reliable method for you to monitor kernel maturity for irrigation scheduling purposes is to observe this progression of the milk-line (or hard starch layer) between dent stage and black-layer. The milk-line is more relevant than the black-layer, because it indicates maturation progress, before the black layer is evident. The milk-line is the borderline between the bright, golden yellow color of the hard seed coat outside the starch, compared to the milky, dull yellow color of the soft seed coat adjacent the dough layer. To observe the milk line, break a corn ear in half and observe the cross-section of the top half of the ear (the side of kernels opposite the embryo). If you have difficulty seeing this color disparity between layers, you can easily find it by simply poking your fingernail into the soft, doughy seed, starting at the kernel base and repeating this procedure progressively toward the tip, until you feel the hard starch.